Summary Of Intelligent Code Reviews Using Deep Learning
Code Review Paper summary - Part 1
- Title: Intelligent code reviews using deep learning
- Authors: Anshul Gupta, Neel Sundaresan
- Link: https://www.kdd.org/kdd2018/files/deep-learning-day/DLDay18_paper_40.pdf
- Tags: Supervised learning, Neural networks, Software functional properties
- Year: 2020
Summary
-
What
-
They build a deep learning-based system in order to recommend a review of the common issues in the codebase. They called their system DeepCodeReviewer(DCR). It used deep learning to learn review relevance to a code snippet and recommend the right review.
-
DCR has been trained on historical peer reviews data from Microsoft’s internal repositories.
-
Previous studies show that even with a strong motivation to find essential defects like bugs and functional issues in code, reviewers tend to focus on reviews related to apparent bugs or best practices. In other words, reviewers got distracted by these common issues. DCR can alleviate this issue by recommending reviews associated with these common issues and let reviewers perform code reviews with highly focus on essential defects.
-
They generated a raepository of reviews based on the previous pull request reviews.
-
For any new Pull Request, they first chucked the code into smaller code snippets. For each of them, they selected a set of reviews candidates from the generated review repository. Finally, they used LSTM in order to predict the most relevant review of the current code snippet.
-
-
How
-
They trained a deep learning model that takes (code, review) pairs as input and produces scores that indicate the relevance of each review and its corresponding code snippet.
- They first applied a preprocessing step in order to remove noise from (code, review) pairs and convert them to a sequence. For any new code snippet, the same preprocessing step has been applied.
-
They used Lexer tokenizer in order to convert codes to a list of (token name, value) pairs, in which the token name in the category of the token(Operators, Name, KeyWord, etc.).
-
They used an NLTK tweet tokenizer to tokenize the review comments.
-
-
To vectorized the sequences which were generated based on Codes and Reviews, they utilized the Word2Vec algorithm. Word2Vec was the right choice since it can preserve the semantic relation between tokens.
-
To generate the input data (C, R), they create relevant(+ve) and non-relevant(-ve) tuples of codes and reviews. The historical PRs reviews only contain (+ve), so they had to generate the non-relevant tuples. They select one relevant pair(let’s call it the current pair) and select four different pairs(let’s call them sampled pairs). Then, they generate new pairs by combining code snippets from the current pair with the review part of sampled pairs. Finally, they used the final version of the code snippet, which was merged to the mainline and its review as a non-relevant pair. Their intuition behind the last part was to make their model learn not to assign the PRs review to the accepted code snippet.
-
The code snippet in each pair was divided into three parts. The first part is the current line, which is the line where the review comment is posted by a reviewer. It divides the code snippet into two parts—the upper and the lower lines.
-
Their model takes these three parts, the review, and the code context, as an input.
- Their proposed Deep Learning model
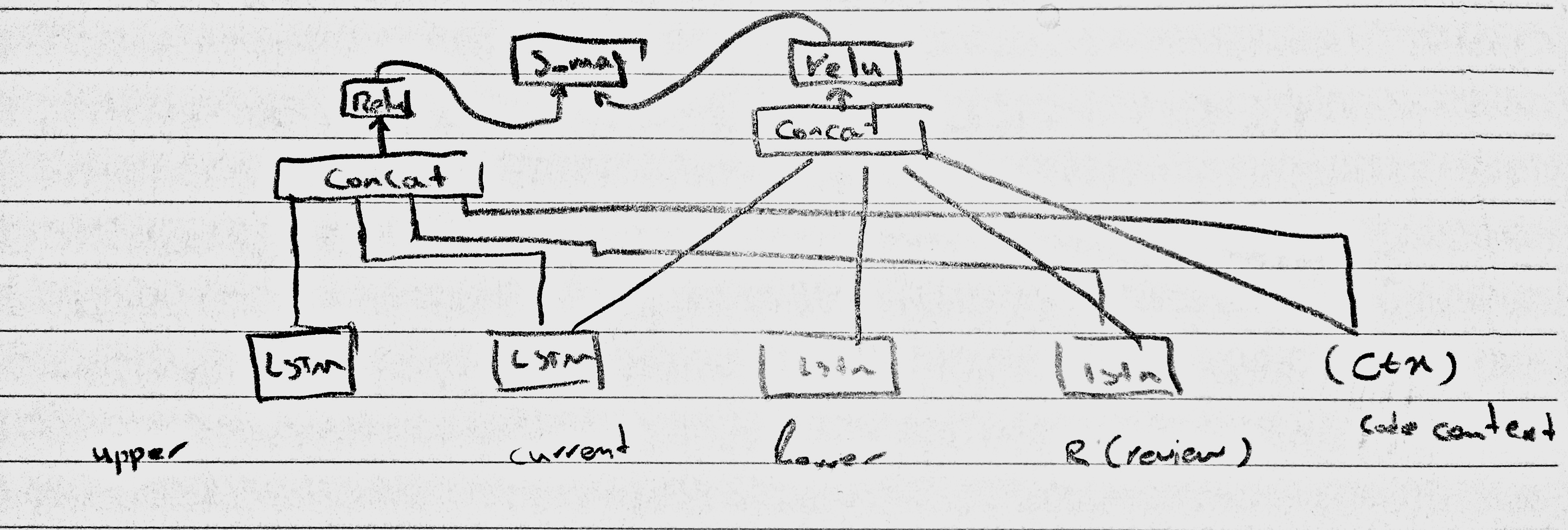
- General workflow:
- When a new PR comes, DCR starts by splitting code files into smaller code snippets.
- For each code snippet, a set of candidate reviews from a repository of reviews are found. 3. Code snippets are paired with each candidate review to create tuples. 4. Preprocessing steps take place. 5. Pass tuples to the model to calculate the relevance score for each candidate. 6. Reviews that cross a certain threshold are the DCR’s recommendations for a code snippet.
- Candidate review selection: First, all parts(upper, current, lower) of the new code snippets will be feed through the LSTMs to get the encoded representation of them. Then, the cosine similarity between the new and all the code snippets in the repository (for all the three parts individually) will be calculated. Finally, the reviews from code snippets similar to new code snippets will be selected as candidates.
-
- Results
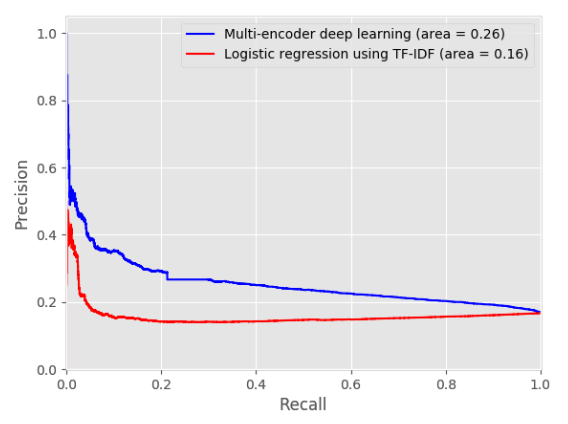
- They used the TF-IDF and logistic regression method as their baseline.
- They randomly generated 49 -ve pairs for each positive pair. Then they calculated the relevance score for all of these 50 pairs and ranked them with that score. They used this ranking to calculate their metrics.
- They used Mean reciprocal rank measures. Mean reciprocal rank measures the ranking quality by assuming that there exists only one relevant review. Hence it penalizes all other reviews apart from the current one.
-
User study
- 77% of their user believed this tool could be helpful, and 66% said they would recommend it to their colleague.
- Their primary contributions: developing a deep learning-based model in order to recommend reviews for common issues.
-
Their primary contributions(what I see): They proposed an acceptable approach to utilize all parts of the code snippet and simultaneously use code context.
- Proposed feature work:
- Train a single model for recommending reviews for different programming languages( can be done by meta-learning!)